Dengue Fever in Bangladesh: How to Protect Yourself
Dengue Fever in Bangladesh is currently experiencing a record outbreak, with a lack of a coordinated response leading to increased deaths from the mosquito-transmitted disease. Bangladesh’s monsoon season, from June to September, provides favorable conditions for the breeding of Aedes mosquitoes, which carry the dengue virus.
Severe dengue symptoms often manifest after the fever subsides and may include abdominal pain, vomiting, bleeding gums, fatigue, and weakness. The World Health Organization (WHO) has called for swift action to address the surge in dengue cases in Bangladesh, as the virus has the potential to cause epidemics with high morbidity and mortality rates.
Despite the absence of specific treatments, early detection can help manage the disease’s impact.
Introduction To Dengue Fever In Bangladesh
Dengue Fever is currently a major public health concern in Bangladesh, with recurring outbreaks and a lack of coordinated response leading to increased fatalities. The country’s monsoon season from June to September provides a favorable breeding ground for mosquitoes, further contributing to the spread of the disease.
Overview Of Dengue Fever In Bangladesh:
- Dengue fever is a prevalent mosquito-borne viral disease in Bangladesh.
- The country has been experiencing prolonged dengue fever outbreaks, which can be attributed to climate change.
- Lack of a coordinated response has led to an increase in deaths from the disease.
- Dengue season in Bangladesh is usually during the monsoon season from June to September.
- The breeding of Aedes mosquitoes, which transmit dengue, is facilitated by the favorable climate conditions during this period.
- The symptoms of dengue can range from mild to severe, with severe cases often presenting with abdominal pain, persistent vomiting, rapid breathing, and bleeding gums or nose.
Importance Of Swift Action To Combat Dengue:
- The World Health Organization (WHO) has urged Bangladesh to take swift action to curb the surge in dengue cases.
- Swift action is vital in preventing further spread of the disease and reducing the number of fatalities.
- Coordinated efforts from all stakeholders, including healthcare providers, government agencies, and the public, are crucial in combating dengue fever effectively.
Impact Of Climate Change On Dengue Fever Outbreaks In Bangladesh:
- Climate change has contributed to prolonged dengue fever outbreaks in Bangladesh.
- Rising temperatures and changing weather patterns have created conducive environments for the breeding and spread of Aedes mosquitoes, the primary carriers of the dengue virus.
- Increased rainfall during the monsoon season results in stagnant water, which serves as breeding grounds for mosquitoes.
- Efforts to mitigate climate change and control mosquito populations are necessary to minimize the impact of dengue fever in Bangladesh.
Coordinated Response Against Dengue Fever:
- To effectively combat dengue fever in Bangladesh, a coordinated response is crucial.
- This includes proactive mosquito control measures, such as the elimination of stagnant water sources and the use of insecticides.
- Public awareness campaigns on dengue prevention and early recognition of symptoms play a significant role in reducing the spread of the disease.
- Strengthening healthcare systems and improving access to medical care are also essential in managing dengue cases effectively.
Dengue fever is a significant public health concern in Bangladesh, particularly during the monsoon season. The country faces challenges in controlling dengue outbreaks due to climate change and a lack of coordinated response. Swift action, including proactive mosquito control measures and public awareness campaigns, is crucial to combat this mosquito-borne disease effectively.
Efforts to mitigate climate change and strengthen healthcare systems will contribute to reducing the impact of dengue fever in Bangladesh.
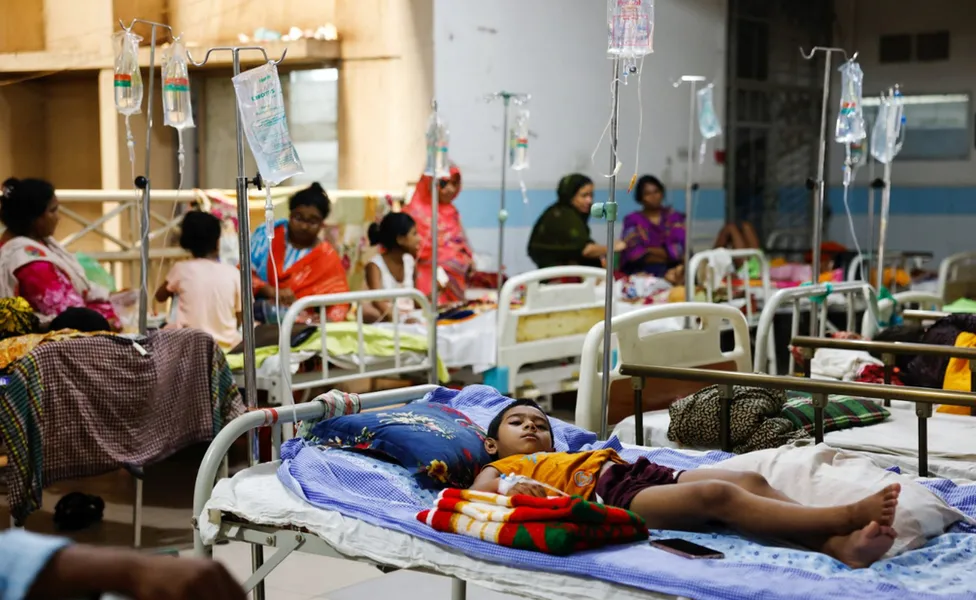
Credit: BBC Photo
Epidemiology Of Dengue In Bangladesh
The epidemiology of dengue in Bangladesh shows a significant surge in cases of dengue fever, with a lack of a coordinated response causing more deaths from the mosquito-transmitted disease. The country experiences recurrent outbreaks, particularly during the June-to-September monsoon season when mosquitoes thrive in stagnant water, leading to high morbidity and mortality rates.
WHO has urged swift action to address this growing public health concern.
Dengue fever, a mosquito-borne viral disease, has been a significant health concern in Bangladesh for several years. Here is an overview of the epidemiology of dengue in the country:
- Dengue is endemic in Bangladesh, with regular outbreaks occurring each year during the monsoon season.
- The majority of dengue cases in Bangladesh are reported between June and September when the Aedes mosquitoes, responsible for transmitting the virus, are most active.
- The climate in Bangladesh, characterized by high temperatures and humidity, provides a favorable environment for the breeding of Aedes mosquitoes.
- Over the years, the number of dengue cases in Bangladesh has seen an alarming increase, with several outbreaks reaching epidemic proportions.
- The most affected regions in Bangladesh include Dhaka, Chattogram, and Sylhet.
- Lack of proper sanitation and inadequate waste management contribute to the proliferation of mosquito breeding sites in urban areas.
- The dengue virus has four serotypes, and individuals infected with one serotype are not immune to the others, which increases the likelihood of severe infections.
- Symptoms of dengue in Bangladesh include high fever, severe headache, joint and muscle pain, rash, and in severe cases, dengue hemorrhagic fever or dengue shock syndrome.
- The government of Bangladesh has taken several steps to control dengue, including implementing vector control measures, raising awareness about preventive measures, and improving healthcare facilities to handle dengue cases.
- Climate change, urbanization, and population growth contribute to the increasing dengue burden in Bangladesh.
The epidemiology of dengue in Bangladesh highlights the ongoing challenges faced by the country in controlling the disease. Efforts to prevent dengue transmission, improve healthcare services, and raise awareness among the population are essential to minimize the impact of dengue outbreaks.
Dengue Virus And Transmission
Dengue fever outbreaks in Bangladesh have been prolonged due to climate change, increasing the risk of more infections during the monsoon season. The lack of a coordinated response has caused more deaths from this mosquito-transmitted disease, making it a major public health concern in the country.
Dengue fever is caused by the dengue virus, which is transmitted through the bite of infected Aedes mosquitoes, mainly the Aedes aegypti species. These mosquitoes become infected when they bite a person who already has the virus in their bloodstream, and then they can transmit the virus to other individuals they bite.
Here are some key points about the dengue virus and its transmission:
- The dengue virus belongs to the Flaviviridae family and has four distinct serotypes, known as DENV-1, DENV-2, DENV-3, and DENV-4. Each serotype can cause dengue fever, and subsequent infections with different serotypes can lead to more severe forms of the disease.
- Mosquitoes become infected with the dengue virus when they feed on the blood of a person with dengue fever during the first few days of the illness.
- Once infected, the mosquito remains a carrier of the virus for their entire life, which can be up to a month.
- Female Aedes mosquitoes, which are responsible for dengue transmission, lay their eggs in containers or areas with stagnant water, such as flowerpots, discarded tires, and open water tanks.
- The eggs can survive in dry conditions for several months, waiting for favorable conditions to hatch, such as rainfall or the presence of water.
- The mosquito larvae hatch from the eggs and develop into pupae and then into adults, ready to bite and transmit the virus to humans.
- The Aedes mosquitoes are primarily active during the day, with their peak biting periods occurring in the early morning and late afternoon.
- Dengue virus cannot be directly transmitted from person to person. Instead, it requires the intermediate vector of the Aedes mosquito for transmission.
- It’s important to note that while dengue is primarily transmitted by mosquitoes, there have been rare cases of transmission through blood transfusions, organ transplants, and vertical transmission from a pregnant woman to her fetus.
Understanding the virus and its mode of transmission is crucial for effective preventive measures and control strategies. By focusing on mosquito control and reducing breeding sites, we can help minimize the spread of dengue fever and protect public health.
Symptoms And Clinical Presentation
Dengue fever in Bangladesh is characterized by symptoms such as severe abdominal pain, persistent vomiting, bleeding gums or nose, fatigue, and pale and cold skin. The country is currently facing a record outbreak, and immediate action is needed to combat the mosquito-transmitted disease.
Dengue fever is a mosquito-borne viral infection that can cause a range of symptoms. Here are the common symptoms and clinical presentations associated with dengue fever in Bangladesh:
- Fever: The hallmark symptom of dengue fever is a high fever that can reach up to 104°F (40°C). The fever is usually sudden in onset and can last for 2 to 7 days.
- Headache: Many individuals with dengue fever experience severe headaches, which can be persistent and throbbing.
- Muscle and joint pain: Dengue fever commonly causes muscle and joint pain, giving rise to the term “breakbone fever.” The pain can be severe and affect multiple joints in the body.
- Nausea and vomiting: Nausea and vomiting are common symptoms of dengue fever. These symptoms can be particularly debilitating and may persist throughout the febrile phase of the illness.
- Rash: A rash may develop on the skin of individuals with dengue fever. The rash can be itchy and usually appears after the fever subsides.
- Fatigue: Dengue fever often leads to extreme tiredness and fatigue, which can persist for weeks after the acute phase of the illness.
- Bleeding: In severe cases, dengue fever can cause internal bleeding and external bleeding manifestations. This can include bleeding gums, nosebleeds, and blood in the urine or stool.
- Abdominal pain: Some individuals with dengue fever experience severe abdominal pain, which can be accompanied by persistent vomiting.
- Respiratory symptoms: Dengue fever can also cause respiratory symptoms such as rapid breathing and shortness of breath, especially in severe cases.
It’s important to note that symptoms may vary from person to person, and not all individuals infected with dengue fever will experience all these symptoms. If you experience any of these symptoms and live in an area with dengue transmission, it is advisable to seek medical attention promptly.
Remember, early detection and proper management of dengue fever are crucial for a favorable outcome.
Diagnosis And Laboratory Testing
Diagnosis and Laboratory Testing for dengue fever in Bangladesh play a crucial role in identifying and managing the disease. Early and accurate diagnosis is essential to provide appropriate treatment and prevent further spread of the virus. Through laboratory tests, healthcare professionals can confirm the presence of dengue fever and determine the severity of the infection.
In order to diagnose dengue fever in Bangladesh, healthcare professionals rely on a combination of clinical assessments and laboratory testing. Here’s a breakdown of the diagnostic methods used:
- Clinical Assessments:
- Doctors evaluate the patient’s symptoms and medical history to determine the likelihood of dengue fever.
- Common symptoms include high fever, severe headache, joint and muscle pain, rash, and mild bleeding from the nose or gums.
- The presence of symptoms during the dengue season in Bangladesh increases suspicion of the disease.
- It’s important to note that dengue fever symptoms can be similar to other viral infections, so laboratory testing is crucial for confirmation.
- Laboratory Testing:
- Blood tests are the main laboratory diagnostic tool for dengue fever.
- The two primary tests used are the NS1 antigen test and the IgM antibody test.
- The NS1 antigen test detects the viral protein in a patient’s blood within the first few days of infection.
- The IgM antibody test looks for antibodies produced by the body to fight dengue virus and is usually performed after the first week of symptoms.
- In some cases, the IgG antibody test may also be performed to detect a past dengue infection.
- These tests are generally conducted in specialized laboratories or hospitals equipped with the necessary facilities.
- Importance of Timely Diagnosis:
- Early diagnosis is crucial for managing dengue fever effectively and preventing complications.
- It helps healthcare professionals provide appropriate care and monitor the patient closely.
- Timely diagnosis also helps in implementing vector control measures to prevent the spread of dengue virus.
Remember, if you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms of dengue fever, it is essential to consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment. Early detection can make a significant difference in the outcome of the disease.
Treatment And Management
Dengue Fever in Bangladesh requires prompt treatment and effective management. With recurrent outbreaks and a lack of coordinated response, experts suggest that addressing the mosquito-transmitted disease is crucial to reducing fatalities and preventing future epidemics.
Dengue fever is a serious viral illness that requires prompt medical care. Proper treatment and management are crucial in preventing complications and ensuring a smooth recovery. Here are some key points to consider:
- Hospitalization: Severe cases of dengue fever may require hospitalization. This allows healthcare professionals to closely monitor the patient’s condition and provide necessary treatments.
- Fluid replacement: One of the main goals of dengue fever treatment is to maintain fluid balance in the body. Intravenous fluid replacement therapy is commonly used to prevent dehydration and restore electrolyte levels.
- Symptom relief: Medications such as acetaminophen can be used to alleviate fever and pain. However, it is important to avoid nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) as they can increase the risk of bleeding.
- Monitoring platelet count: Dengue fever can lead to a decrease in platelet count, which increases the risk of bleeding. Regular blood tests are conducted to monitor platelet levels and take necessary precautions.
- Rest and recovery: Adequate rest is essential for the body to fight off the infection. Patients are advised to take plenty of rest and avoid strenuous activities until they have completely recovered.
- Prevention of mosquito bites: While there is no specific antiviral treatment for dengue fever, preventing mosquito bites is crucial to avoid further transmission. This includes using insect repellents, wearing protective clothing, and using mosquito nets.
- Follow-up care: After being discharged from the hospital, patients should continue to monitor their symptoms and seek medical attention if they worsen. Regular follow-up visits may be necessary to ensure a full recovery.
Remember, early diagnosis and proper treatment are key to managing dengue fever effectively. If you suspect you have dengue fever or are experiencing severe symptoms, seek medical attention immediately.
Prevention And Control Strategies
Prevention and control strategies for combating Dengue Fever in Bangladesh are essential to curb the outbreak. These strategies include eliminating mosquito breeding sites, using mosquito repellent, wearing protective clothing, and promoting public awareness campaigns on prevention measures.
Dengue fever is a widespread problem in Bangladesh, but there are several prevention and control strategies that can help reduce its impact. These strategies include:
- Eliminating mosquito breeding sites: Mosquitoes that carry the dengue virus, such as the Aedes mosquito, breed in stagnant water. By regularly checking and emptying containers that can collect water, such as buckets, flowerpots, and tires, we can greatly reduce the breeding grounds for mosquitoes.
- Using mosquito repellents: Applying mosquito repellents, especially those containing DEET, can provide protection against mosquito bites. It is important to follow the instructions on the product and reapply as necessary.
- Wearing protective clothing: Wearing long sleeves, pants, and socks can provide physical barriers against mosquito bites. This is especially important during peak mosquito activity times, which are usually early morning and late afternoon.
- Installing window screens: Installing window screens can help keep mosquitoes out of homes and buildings, reducing the risk of dengue transmission. It is important to make sure the screens are properly fitted and free from holes.
- Using bed nets: Sleeping under insecticide-treated bed nets can provide protection against mosquito bites while sleeping. This is particularly important for infants, young children, and pregnant women who may spend more time indoors.
- Community involvement: Engaging the community in dengue prevention efforts is crucial. Conducting awareness campaigns, distributing educational materials, and encouraging community members to take part in clean-up activities can help raise awareness and promote behavioral change.
- Improving sanitation: Ensuring proper waste management and maintaining clean surroundings can help reduce the breeding sites for mosquitoes. Regular garbage collection and proper disposal of waste can contribute to the overall control of dengue.
- Strengthening healthcare systems: Building capacity within healthcare systems to diagnose and treat dengue cases is essential. Training healthcare providers, ensuring access to diagnostic tools, and improving surveillance systems can help in early detection and management of dengue cases.
By implementing these prevention and control strategies, Bangladesh can effectively combat dengue fever, reduce the number of cases, and minimize the impact of this disease on its population.
Government Response And Healthcare Infrastructure
Bangladesh is experiencing a record outbreak of dengue fever, and experts emphasize the need for a coordinated response to address the mosquito-transmitted disease. The country’s healthcare infrastructure is facing challenges in handling the prolonged outbreak, exacerbated by climate change.
The government of Bangladesh has taken several measures to address the dengue fever outbreak and improve healthcare infrastructure in the country. These include:
- Awareness campaigns: The government has launched extensive awareness campaigns to educate the public on dengue prevention, symptoms, and treatment options. These campaigns aim to empower individuals to take necessary precautions and seek prompt medical attention.
- Vector control: The government has implemented rigorous vector control measures, such as mosquito breeding site monitoring and insecticide spraying. This helps to minimize the breeding and spread of dengue-carrying mosquitoes in high-risk areas.
- Sufficient healthcare facilities: The government has increased the number of healthcare facilities dedicated to treating dengue cases. This includes setting up specialized dengue treatment centers and allocating additional resources to existing hospitals to accommodate the influx of patients.
- Enhanced medical capacity: The government is continually working to improve the medical capacity of healthcare professionals in diagnosing and treating dengue cases. This includes training programs and workshops to enhance knowledge and skills in dengue management.
- Collaboration with international organizations: The government has actively collaborated with international organizations, such as the World Health Organization (WHO), to access expertise, resources, and funding to strengthen their response to the dengue outbreak.
- Improvement in healthcare infrastructure: The government is investing in improving healthcare infrastructure across the country, particularly in rural areas. This includes the construction of new hospitals, upgrading existing facilities, and ensuring access to essential medical equipment and supplies.
- Research and development: The government is actively supporting research and development initiatives focused on better understanding the dengue virus and developing effective treatments and vaccines. This includes collaborating with local universities and research institutions to drive innovation in the field of dengue research.
By implementing these measures, the government of Bangladesh aims to effectively respond to the dengue fever outbreak and ensure that individuals have access to quality healthcare services. These efforts are crucial in minimizing the impact of dengue and reducing the number of fatalities associated with the disease.
Research And Innovation
The ongoing outbreak of Dengue Fever in Bangladesh is a pressing concern caused by climate change. Experts stress the need for swift action and a coordinated response to reduce the number of deaths from this mosquito-transmitted disease.
In recent years, Bangladesh has seen an alarming rise in dengue fever cases. To combat this deadly disease, researchers and innovators in the country have been working tirelessly to develop new strategies and solutions. Here are some advancements in research and innovation that aim to tackle dengue fever in Bangladesh:
- Improved diagnostics: Researchers have been focusing on developing more accurate and efficient diagnostic tools for dengue fever. This includes the use of rapid diagnostic tests that can quickly detect the presence of dengue virus in a patient’s blood.
- Vaccine development: Scientists in Bangladesh have been actively involved in the development of a dengue vaccine. This vaccine aims to provide immunity against all four serotypes of the dengue virus, offering long-term protection against the disease.
- Mosquito control initiatives: Innovations in mosquito control methods have been a priority in Bangladesh. Scientists have been exploring new technologies, such as genetically modified mosquitoes and insecticide-laden traps, to effectively reduce the mosquito population and prevent the spread of dengue.
- Public awareness campaigns: Researchers have recognized the importance of educating the public about dengue prevention. Through the use of media campaigns and community outreach programs, they aim to raise awareness about mosquito breeding sites, proper hygiene practices, and the importance of seeking medical help at the early stages of the disease.
- Climate change adaptation: As climate change continues to exacerbate the spread of dengue fever, researchers in Bangladesh are studying the relationship between climate patterns and dengue outbreaks. This knowledge allows for better prediction and preparedness measures to be implemented in vulnerable areas.
- Collaborative efforts: Research institutions, universities, and governmental bodies are collaborating to address the ongoing dengue crisis in Bangladesh. By pooling their resources and expertise, they can develop comprehensive strategies to control the disease and minimize its impact on public health.
These research and innovation initiatives offer hope in the fight against dengue fever in Bangladesh. By combining scientific advancements with community engagement and proactive measures, the country can work towards reducing the prevalence of this deadly disease.

Credit: m.youtube.com
Frequently Asked Questions For Dengue Fever In Bangladesh
Does Bangladesh Have Dengue?
Yes, Bangladesh is currently experiencing a record outbreak of dengue fever, causing significant health concerns.
When Is The Dengue Season In Bangladesh?
The dengue season in Bangladesh occurs during the June-to-September monsoon season.
When Is Mosquito Season In Bangladesh?
The mosquito season in Bangladesh, favorable for breeding of Aedes mosquitoes, is during the June-to-September monsoon season.
What Are The Symptoms Of Dengue In Bangladesh?
Symptoms of dengue in Bangladesh include abdominal pain, vomiting, bleeding gums/nose, fatigue, and pale/cold skin.
Conclusion
The current outbreak of dengue fever in Bangladesh has become a serious public health concern. The lack of a coordinated response has resulted in a record number of deaths from this mosquito-transmitted disease. The prolonged outbreaks can be attributed to climate change, as the monsoon season creates a favorable environment for the breeding of Aedes mosquitoes.
It is crucial that swift action is taken to control the spread of dengue fever in Bangladesh. Early detection and treatment are vital in minimizing the severity of the symptoms and preventing further complications. The World Health Organization (WHO) has emphasized the need for effective measures to curb the surge in dengue cases.
It is crucial to raise awareness about the symptoms of dengue and promote preventive measures such as eliminating stagnant water where mosquitoes breed. By implementing these measures, we can work towards reducing the impact of dengue fever and protecting the health of the people of Bangladesh.